
The Cold War was a period of political and military tension between the Western powers, led by the United States, and the Eastern powers, led by the Soviet Union. This conflict lasted from the end of World War II in 1945 until the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991. It was called the Cold War because there was no direct military conflict between the two sides. Instead, they engaged in a series of proxy wars, arms races, and political maneuvering that brought the world to the brink of nuclear war on several occasions.
The End of World War II

The end of World War II marked the beginning of the Cold War. The Soviet Union and the Western powers had been allies during the war, but they had very different ideas about how to rebuild Europe and the rest of the world. The Soviet Union wanted to spread communism throughout the world, whereas the Western powers wanted to promote democracy and free market capitalism.
The Iron Curtain
In 1946, the Soviet Union's leader, Joseph Stalin, gave a speech in which he described the division between the Soviet Union and the West as an "Iron Curtain." This term became a symbol for the division between the communist East and the capitalist West. The Iron Curtain separated the Soviet Union and its allies from the rest of the world, both physically and ideologically.
The Truman Doctrine

In 1947, President Harry Truman of the United States announced the Truman Doctrine. This policy stated that the United States would provide military and economic assistance to any country threatened by communism. The Truman Doctrine was a direct response to the Soviet Union's attempt to spread communism throughout the world.
The Marshall Plan

Also in 1947, Secretary of State George Marshall announced the Marshall Plan. This was a program that provided economic aid to Western European countries that had been devastated by World War II. The goal of the Marshall Plan was to rebuild these countries with capitalism and democracy, and to prevent them from falling under Soviet control.
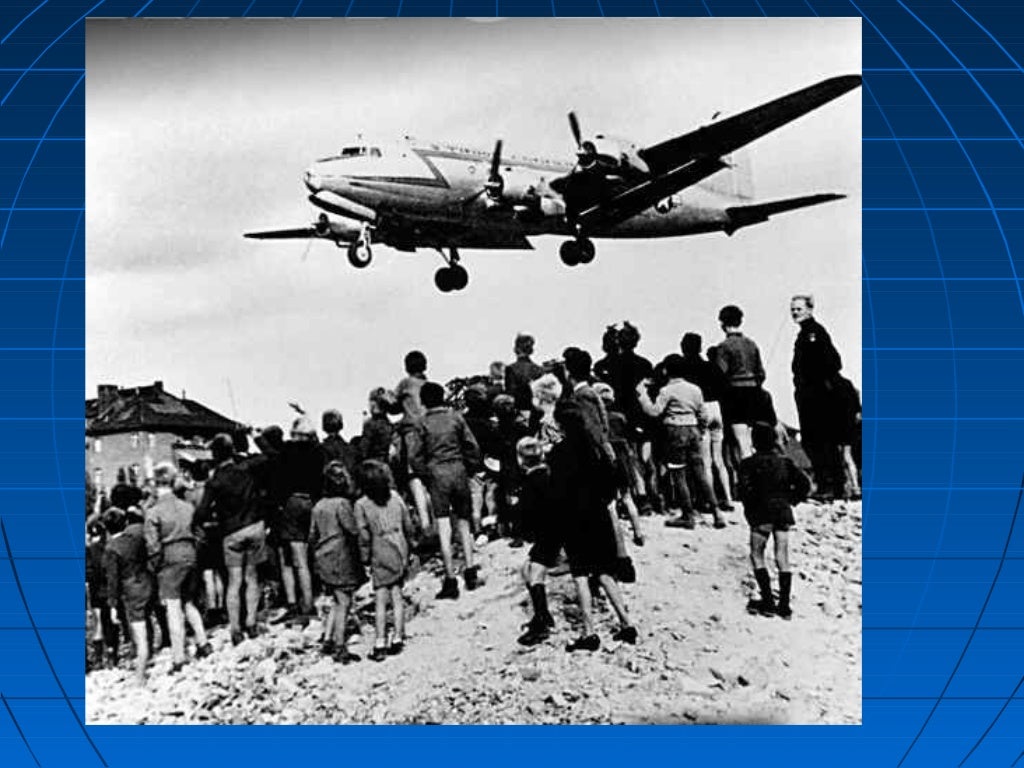
The Berlin Blockade and Airlift
In 1948, the Soviet Union blockaded the city of Berlin, which was located in the Soviet-controlled area of Germany. The goal of the blockade was to force the Western powers out of Berlin. Instead of leaving, the United States and its allies organized an airlift to bring supplies to the people of Berlin. This airlift lasted for almost a year and was a major victory for the Western powers.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)

In 1949, the Western powers formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). This was a military alliance that included the United States, Canada, and several European countries. The goal of NATO was to provide collective defense against the Soviet Union and its allies.
The Warsaw Pact

In 1955, the Soviet Union formed the Warsaw Pact. This was a military alliance that included the Soviet Union and several other communist countries in Eastern Europe. The goal of the Warsaw Pact was to provide collective defense against NATO and the Western powers.
The Arms Race

Throughout the Cold War, both the United States and the Soviet Union engaged in an arms race. They developed and stockpiled nuclear weapons, missiles, and other military technology. The goal of the arms race was to deter the other side from attacking. However, this also created a dangerous climate of fear and mistrust.
The Cuban Missile Crisis

In 1962, the United States discovered that the Soviet Union was secretly installing nuclear missiles in Cuba. This was a major threat to the United States, as Cuba is located just 90 miles from the United States. President John F. Kennedy demanded that the Soviet Union remove the missiles, and the two sides engaged in a tense standoff that lasted for several days. Eventually, the Soviet Union agreed to remove the missiles, and the crisis was averted.
The Fall of the Soviet Union

In 1991, the Soviet Union dissolved, bringing an end to the Cold War. The fall of the Soviet Union was the result of a combination of factors, including economic problems, political corruption, and pressure from the West. The end of the Cold War marked a major shift in the balance of power in the world, and it had a profound impact on global politics and international relations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Cold War was a complex and multifaceted conflict that lasted for almost half a century. It was sparked by a combination of ideological differences, political maneuvering, and military buildup. Despite the fact that there was no direct military conflict between the two sides, the Cold War had a profound impact on the world and brought it to the brink of nuclear war on several occasions.