Japan is a country that is situated in the Pacific Ocean and consists of a chain of islands. The country is home to more than 100 active volcanoes, which is the highest number of active volcanoes in the world. This raises the question, why does Japan have so many volcanoes?
Location

Japan is located in the Pacific Ring of Fire, which is an area where the tectonic plates meet. The Pacific Ring of Fire is known for its volcanic and seismic activities. This means that Japan is situated in a region that is highly prone to volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
Tectonic Plates
Japan is located on the boundary of four tectonic plates. These plates are the Pacific Plate, North American Plate, Eurasian Plate, and Philippine Sea Plate. The movement of these plates is responsible for creating the volcanic activity in Japan. When two plates collide, one of them is forced underneath the other, which creates pressure and heat. This pressure and heat cause the rock to melt and rise to the surface, which results in the formation of volcanoes.
The Pacific Plate

The Pacific Plate is the largest and most active tectonic plate in the world. It is responsible for creating most of the volcanic activity in Japan. The Pacific Plate is subducting beneath the North American Plate, Eurasian Plate, and Philippine Sea Plate, which causes the formation of volcanoes.
The Ring of Fire
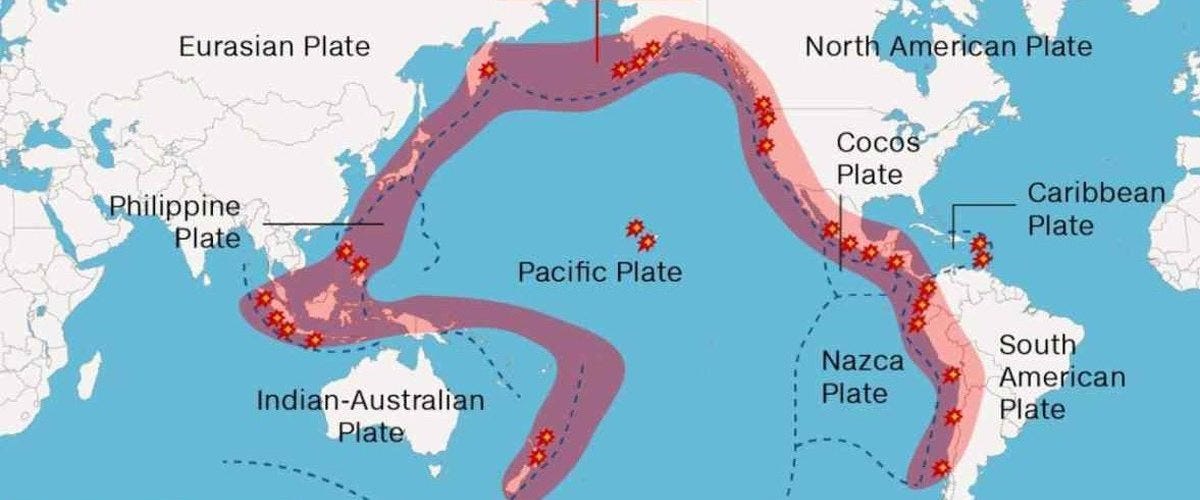
The Ring of Fire is a region around the Pacific Ocean that is highly prone to volcanic and seismic activities. Japan is located in the Ring of Fire, which is one of the reasons why it has so many volcanoes. The Ring of Fire is responsible for creating 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes.
Types of Volcanoes

Japan has different types of volcanoes, which include shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes, and caldera volcanoes. Shield volcanoes are flat and have a gentle slope. Stratovolcanoes are tall and steep, and they are the most dangerous. Caldera volcanoes are large, circular depressions that form after a volcanic eruption.
Volcanic Eruptions

Japan has experienced several volcanic eruptions throughout its history. Some of the most notable eruptions include the eruption of Mount Fuji in 1707, which caused widespread damage, and the eruption of Mount Ontake in 2014, which killed 57 people.
Volcano Monitoring

Japan has a well-established volcano monitoring system, which includes monitoring seismic activities, gas emissions, and ground deformation. This system helps to predict volcanic eruptions and issue warnings to the public.
Conclusion
Japan has so many volcanoes because of its location in the Pacific Ring of Fire, the movement of tectonic plates, and the presence of the Pacific Plate. Japan's volcanic activity has resulted in the formation of different types of volcanoes and several volcanic eruptions throughout its history. However, Japan's well-established volcano monitoring system helps to predict volcanic eruptions and keep people safe.